Datacamp Course Note - Machine Learning for Marketing in Python
- 3 minsDatacamp - Machine Learning for Marketing in Python
Types of machine learning
Supervised learning
-
Given X, can we predict Y?
-
Classication - when Y is categorical (e.g. Churned/Not-churned, Yes/No, Fish/Dog/Cat).
-
Regression - when Y is continuous (e.g. Purchases, Clicks, Time Spent on Website)
Unsupervised learning
Given X, can we detect patterns and clusters that are homogenous
Reinforcement learning
Given a current state and a number potential actions, which path maximizes the reward
Preprocessing
Exploring churn distribution
telcom.groupby(['Churn']).size() / telcom.shape[0] * 100
Separate features and target variables
target = ['Churn']
custid = ['customerID']
cols = [col for col in telcom.columns if col notin custid + target
Feature Engineering
Aggregation
# Define the snapshot date
NOW = dt.datetime(2011,11,1)
# Calculate recency by subtracting current date from the latest InvoiceDate
features = online_X.groupby('CustomerID').agg({
'InvoiceDate': lambda x: (NOW - x.max()).days,
# Calculate frequency by counting unique number of invoices
'InvoiceNo': pd.Series.nunique,
# Calculate monetary value by summing all spend values
'TotalSum': np.sum,
# Calculate average and total quantity
'Quantity': ['mean', 'sum']}).reset_index()
# Rename the columns
features.columns = ['CustomerID', 'recency', 'frequency', 'monetary', 'quantity_avg', 'quantity_total']
Pivot_table
# Build a pivot table counting invoices for each customer monthly
cust_month_tx = pd.pivot_table(data=online,
values='InvoiceNo',
index=['CustomerID'],
columns=['InvoiceMonth'],
aggfunc=pd.Series.nunique, fill_value=0)
Supervise ML : Implementing Linear Regression
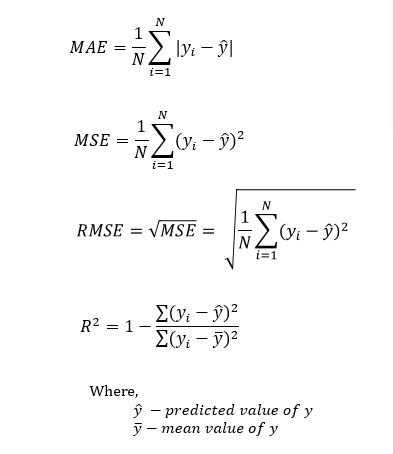
Key Metrics
-
RMSE
-
MAE
-
R-square
OLS Rpeort
# Import `statsmodels.api` module
import statsmodels.api as sm
# Initialize model instance on the training data
olsreg = sm.OLS(train_Y, train_X)
# Fit the model
olsreg = olsreg.fit()
# Print model summary
print(olsreg.summary())
Unsupervised ML : Implementing K means
Unskew the data
-
log-transformation
-
Box-Cox transformation
Scale the data
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
scaler = StandardScaler()
scaler.fit(wholesale_boxcox)
wholesale_scaled = scaler.transform(wholesale_boxcox) wholesale_scaled_df = pd.DataFrame(data=wholesale_scaled,
index=wholesale_boxcox.index,
columns=wholesale_boxcox.columns) wholesale_scaled_df.agg(['mean','std']).round()
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
kmeans=KMeans(n_clusters=k)
kmeans.fit(wholesale_scaled_df)
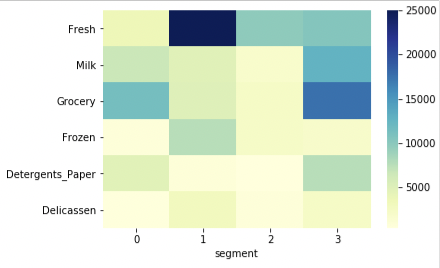
wholesale_kmeans4 = wholesale.assign(segment = kmeans.labels_)kmeans4_averages = wholesale_kmeans4.groupby(['segment']).mean().round(0) print(kmeans4_averages)
sns.heatmap(kmeans4_averages.T, cmap='YlGnBu') plt.show()